The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-SZ)
My current research focuses on Medical Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), with particular applications in forensic medicine and biosignal analysis (e.g., ECG/EEG), under the supervision of Prof. Wang Benyou. During my undergraduate studies, I was honored to be admitted as a visiting student in the Cenbrain Lab at Westlake University, where I worked under the supervision of Prof. Mohamed Sawan. I am also an active contributor to the open-source community, with pull requests to renowned projects such as Areal. My bachelor's thesis was supervised by Dr. Goh Sim Kuan.
I am currently seeking PhD/Intern opportunities. Feel free to drop me an email.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-SZ)MSc in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (M.A.I.R)
Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-SZ)MSc in Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (M.A.I.R)
Rank: 4/117 (Top 3%)Sep. 2024 - Jul. 2026 -
 Xiamen University Malaysia (XMUM)BEng in Software Engineering
Xiamen University Malaysia (XMUM)BEng in Software Engineering
Rank: Top 20%Sep. 2019 - Jul. 2024
Experience
-
 Freedom Intelligence Lab, CUHK-SZPart-time Research Assistant (RA)Oct. 2024 - Present
Freedom Intelligence Lab, CUHK-SZPart-time Research Assistant (RA)Oct. 2024 - Present -
 Cenbrain Lab, Westlake UniversityVisiting Research Assistant (RA)Feb. 2023 - Aug. 2023
Cenbrain Lab, Westlake UniversityVisiting Research Assistant (RA)Feb. 2023 - Aug. 2023 -
 Xiamen Meiya Pico Co., LtdC++/C# EngineerJul. 2022 - Sep. 2022
Xiamen Meiya Pico Co., LtdC++/C# EngineerJul. 2022 - Sep. 2022
Honors & Awards
-
CUHKSZ Entrance Scholarship2024
-
XMUM Distinction Student Award2023
-
XMUM Distinction Student Award2024
Selected Publications (view all )
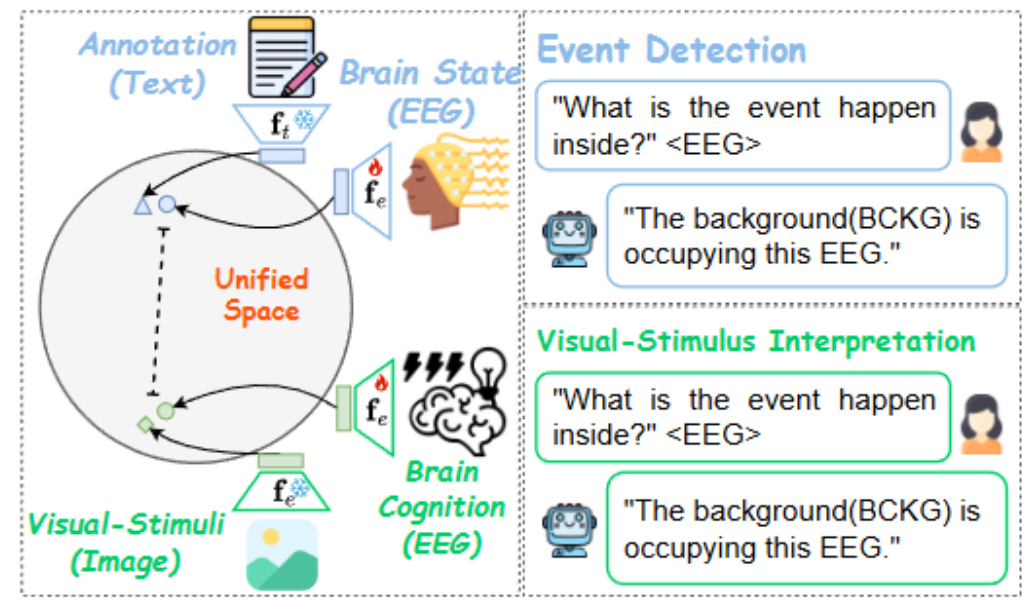
WaveMind: Towards a Generalist EEG Chat Model Aligned to Textual and Visual Modalities
Ziyi Zeng, Zhenyang Cai, Yixi Cai, Xidong Wang, Junying Chen, Rongsheng Wang, Siqi Cai, Haizhou Li, Benyou Wang
Preprint 2025
This study proposes unifying EEG signals and their paired modalities into a shared semantic space to resolve modality mismatch. It introduces WaveMind-Instruct-338k, the first cross-task instruction-tuning EEG dataset, enabling conversational EEG interpretation. The resulting MLLM achieves strong classification performance and supports open-ended dialogue across tasks.
WaveMind: Towards a Generalist EEG Chat Model Aligned to Textual and Visual Modalities
Ziyi Zeng, Zhenyang Cai, Yixi Cai, Xidong Wang, Junying Chen, Rongsheng Wang, Siqi Cai, Haizhou Li, Benyou Wang
Preprint 2025
This study proposes unifying EEG signals and their paired modalities into a shared semantic space to resolve modality mismatch. It introduces WaveMind-Instruct-338k, the first cross-task instruction-tuning EEG dataset, enabling conversational EEG interpretation. The resulting MLLM achieves strong classification performance and supports open-ended dialogue across tasks.
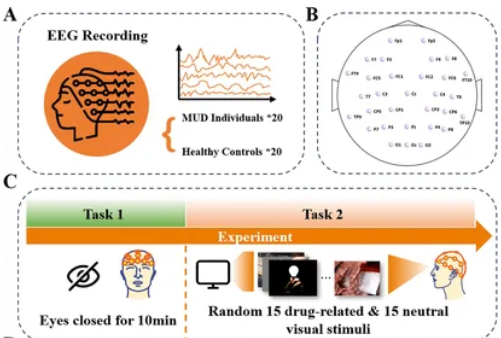
Specific Endophenotypes in EEG Microstates for Methamphetamine Use Disorder
Xurong Gao, Yun-Hsuan Chen, Ziyi Zeng, Wenyao Zheng, Cheng PengChai, Hemmings Wu, Zhoule Zhu, Jie Yang, Lihua Zhong, Hua Shen, Mohamad Sawan
Frontiers in Psychiatry 2025 Accepted
This study applied EEG microstate features classification within EEG across frequency bands and tasks to classify methamphetamine use disorder (MUD) versus controls. The main conclusion involves MUD endophenotyping, pinpointing alpha-band microstate A as a key biomarker.
Specific Endophenotypes in EEG Microstates for Methamphetamine Use Disorder
Xurong Gao, Yun-Hsuan Chen, Ziyi Zeng, Wenyao Zheng, Cheng PengChai, Hemmings Wu, Zhoule Zhu, Jie Yang, Lihua Zhong, Hua Shen, Mohamad Sawan
Frontiers in Psychiatry 2025 Accepted
This study applied EEG microstate features classification within EEG across frequency bands and tasks to classify methamphetamine use disorder (MUD) versus controls. The main conclusion involves MUD endophenotyping, pinpointing alpha-band microstate A as a key biomarker.
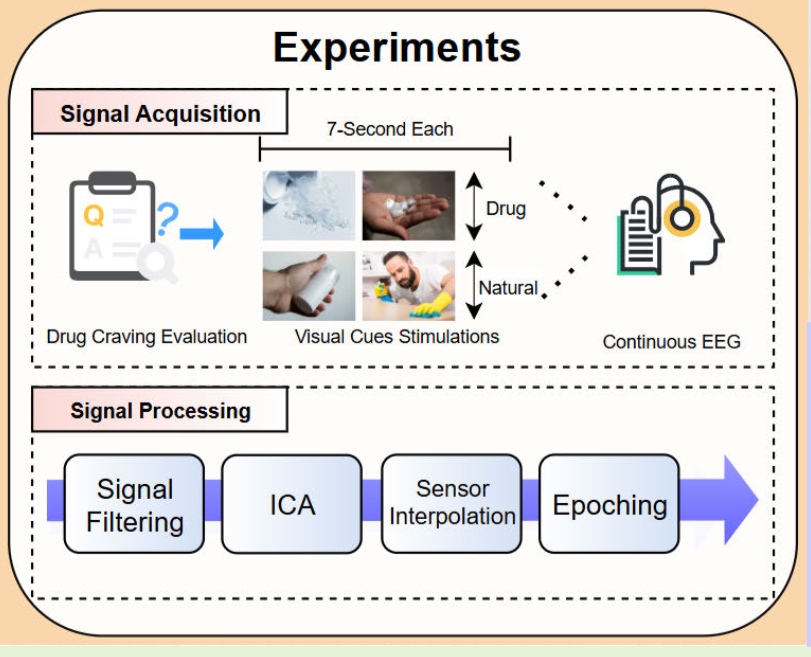
Repetitive TMS-based Identification of Methamphetamine-Dependent Individuals Using EEG Spectra
Ziyi Zeng, Yun-Hsuan Chen, Xurong Gao, Wenyao Zheng, Hemmings Wu, Zhoule Zhu, Jie Yang, Lihua Zhong, Weiwei Cheng, Mohamad Sawan
IEEE Sensors 2025 Accepted
This study uses EEG-based relative band power (RBP) analysis and random forest classification to assess treatment effects in Methamphetamine use disorders (MUD) patients. Gamma RBP was found to be a potential biomarker for rTMS efficacy and a candidate signal for closed-loop neuromodulation in MUD.
Repetitive TMS-based Identification of Methamphetamine-Dependent Individuals Using EEG Spectra
Ziyi Zeng, Yun-Hsuan Chen, Xurong Gao, Wenyao Zheng, Hemmings Wu, Zhoule Zhu, Jie Yang, Lihua Zhong, Weiwei Cheng, Mohamad Sawan
IEEE Sensors 2025 Accepted
This study uses EEG-based relative band power (RBP) analysis and random forest classification to assess treatment effects in Methamphetamine use disorders (MUD) patients. Gamma RBP was found to be a potential biomarker for rTMS efficacy and a candidate signal for closed-loop neuromodulation in MUD.
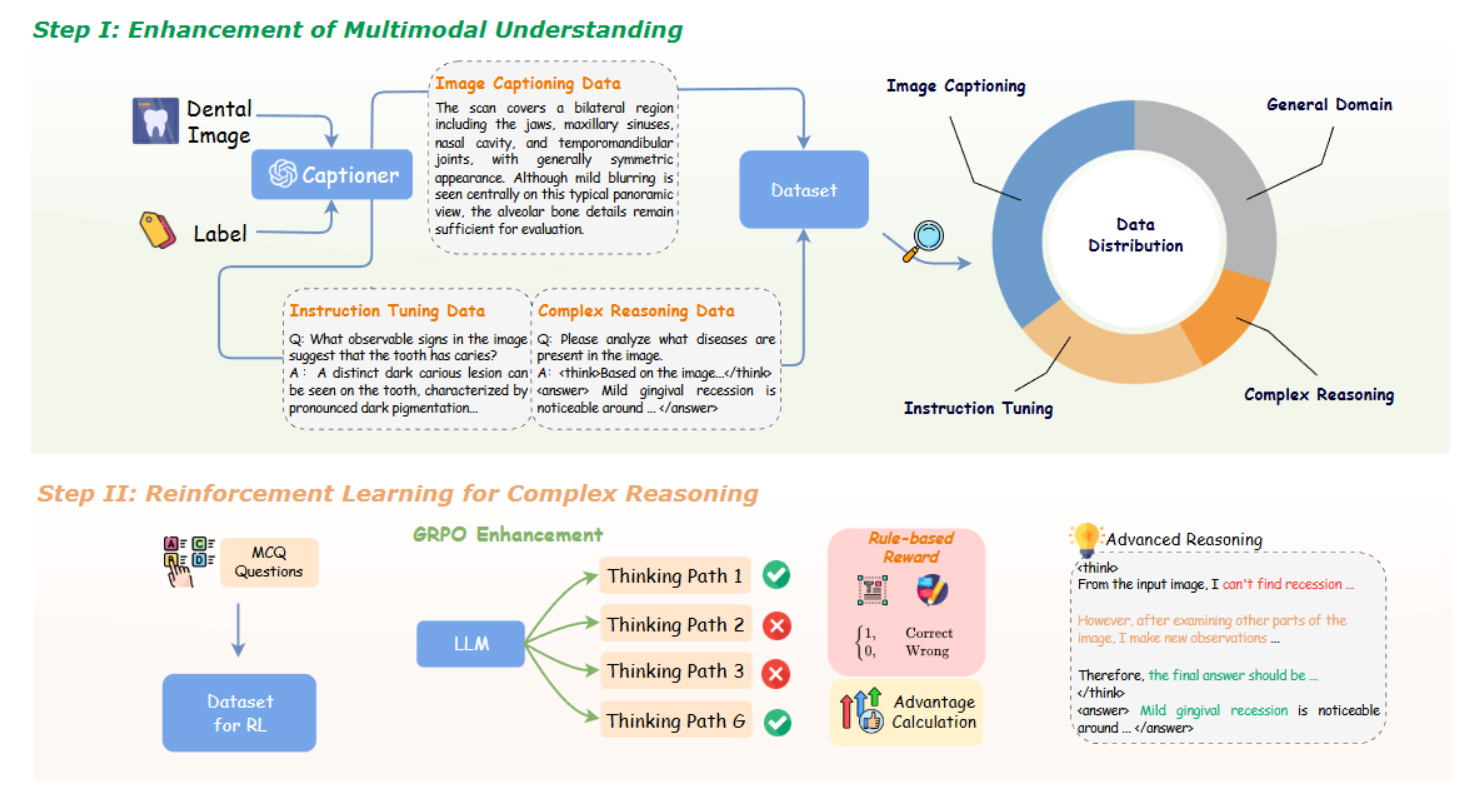
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
Zhenyang Cai, Jiaming Zhang, Junjie Zhao, Ziyi Zeng, Yanchao Li, Jingyi Liang, Junying Chen, Yunjin Yang, Jiajun You, Shuzhi Deng, Tongfei Wang, Wanting Chen, Chunxiu Hao, Ruiqi Xie, Zhenwei Wen, Xiangyi Feng, Zou Ting, Jin Zou Lin, Jianquan Li, Guangjun Yu, Liangyi Chen, Junwen Wang, Shan Jiang, Benyou Wang
arXiv Preprint 2025
DentalGPT is a specialized dental multimodal large language model that addresses limitations in capturing fine-grained dental visual details and performing complex reasoning. Using the largest annotated dental dataset (120k+ images) and reinforcement learning, it achieves superior performance in disease classification and dental VQA tasks, outperforming larger MLLMs with only 7B parameters.
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
Zhenyang Cai, Jiaming Zhang, Junjie Zhao, Ziyi Zeng, Yanchao Li, Jingyi Liang, Junying Chen, Yunjin Yang, Jiajun You, Shuzhi Deng, Tongfei Wang, Wanting Chen, Chunxiu Hao, Ruiqi Xie, Zhenwei Wen, Xiangyi Feng, Zou Ting, Jin Zou Lin, Jianquan Li, Guangjun Yu, Liangyi Chen, Junwen Wang, Shan Jiang, Benyou Wang
arXiv Preprint 2025
DentalGPT is a specialized dental multimodal large language model that addresses limitations in capturing fine-grained dental visual details and performing complex reasoning. Using the largest annotated dental dataset (120k+ images) and reinforcement learning, it achieves superior performance in disease classification and dental VQA tasks, outperforming larger MLLMs with only 7B parameters.